An attribute defines a variable that can be attached to the instances of a class (see Class Attributes) or to a package (see Free Attributes).
Attributes attached to a class are present in each instance of the class, except for a static class attribute, which exists in one copy only, regardless of the number of class instances. In C/C++, non-static class attributes correspond to data members of a struct/class.
A class attribute can only be added to a Class. To add a class attribute, in the Model Explorer right-click on the Class to which you want to add a new class attribute and select Add Attribute from the popup menu.
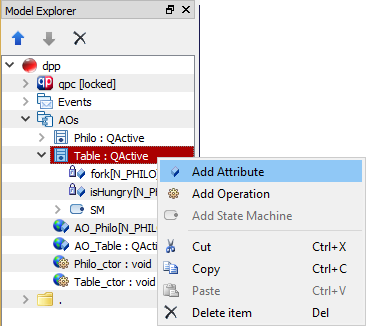
A Class Attribute item can be configured by the Class-Attribute-Specific Property Sheet.
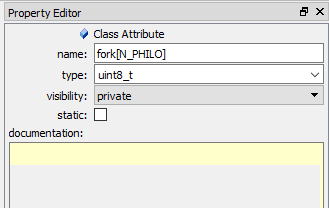
The class-attribute-item property sheet allows you to set the following properties:
public, protected, privateAttributes attached to a package (as opposed to a class) are called free attributes. In C/C++, such free attributes correspond to variables defined directly at file scope (either static variables or a global variables).
A free attribute can only be added to a Package. To add a free attribute, in the Model Explorer right-click on the Package to which you want to add a new free attribute and select Add Attribute from the popup menu.
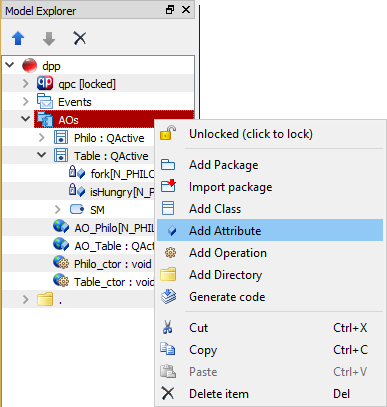
A Free Attribute item can be configured by the Free-Attribute-Specific Property Sheet.
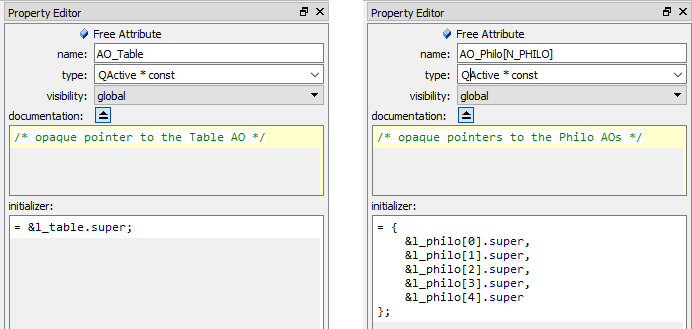
The free-attribute-item property sheet allows you to set the following properties:
As mentioned in the previous section, the Free Attribute Property Sheet, provides the attribute initializer field for an optional initialization of the free attribute at the point of definition. If specified, the attribute initializer is copied literally immediately after the attribute definition (see also $define${}).
For example, the free attribute initializer shown on the left-hand side of the Free Attribute Property Sheets above generates the following code (directive $define${AOs::AO_Table}):
The free attribute initializer shown on the right-hand side of the Free Attribute Property Sheets above generates the following code (directive $define${AOs::AO_Philo[N_PHILO]}):