Operations attached to a class can access individual instances of the class, except for a static class operation, which cannot access any particular instance.
In C, a non-static class operation corresponds to a function that (by a coding convention) takes the "me" pointer to the struct with class attribute (e.g., bool Calc_eval(Calc * const me, double op, uint8_t oper)).
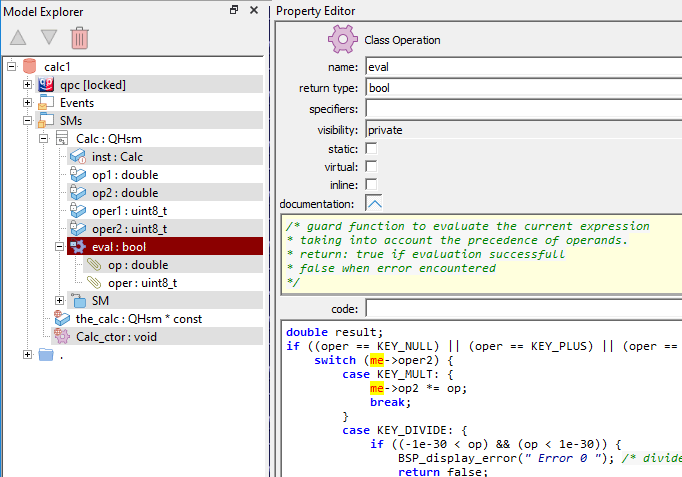
In C++, a non-static class operation corresponds to a class member function, that is a function with the "this"-calling convention (e.g., (e.g., bool Calc::eval(double op, std::uint8_t oper)).
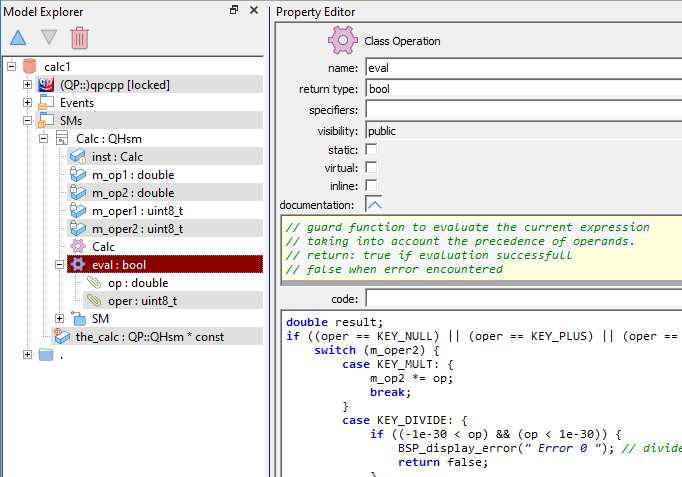
A constructor is a special kind of class operation that initializes an instance of its class. QM supports class constructors both for C and C++.
In C, a constructor should be named ctor, or ctor1, ctor2, etc. if you have more constructors with different signatures (different parameters). The ctor function should have return type void. It can have any number of parameters.
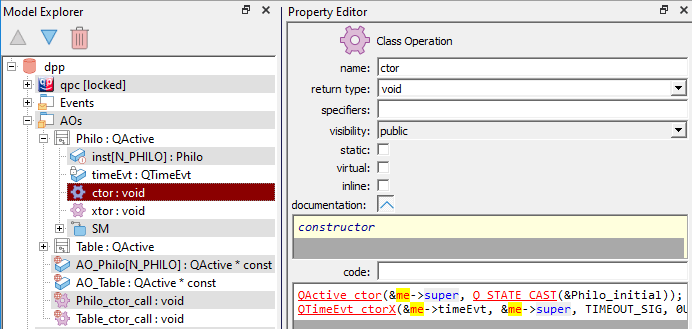
This piece of the model generates the following code:
Philo_ctor() in the listing above calls the superclass' constructor QActive_ctor() as well as member constructor QTimeEvt_ctorX().In C, constructors of global/static objects are not invoked automatically, as is the case in C++. Therefore, in C, you need to call the constructors of all your global/static objects explicitly. This often poses a problem with encapsulation of components, such as Active Objects, where you don't want to expose the whole class declaration (to get to the constructor). In these cases, the example models in QP/C use an idiom, in which the special free operation <Class>_ctor_caller() (or just <Class>_ctor()) is provided just to call the constructor.
For example, the model in the screen shot above contains the free operation Philo_ctor_call(), which is defined as follows
This particular "ctor call" invokes constructors of all Philo instances in the system. Later, in the main() function, only the Philo_ctor_call() operation is called, without exposing the declaration of the Philo class (and its constructor):
In C++, a constructor has the same name as the class and no return value. A constructor can have any number of parameters and a class may have any number of overloaded constructors. Constructors may have any accessibility: public, protected or private.
To provide the constructor initializer list, you put the list in the code panel starting with the colon (':') optionally preceded by any number of spaces. You can continue the list for as many lines as you wish.
The constructor initializer list might be followed by the body of the constructor. To start the body, you simply leave one (or more) empty lines after the initializer. QM will interpret all lines of code after such an empty line as the body of the constructor.
Finally, you might skip the constructor initializer list altogether by simply not placing the colon (':') at the beginning.
The following screen shot shows a C++ constructor with a constructor initializer list and a body.
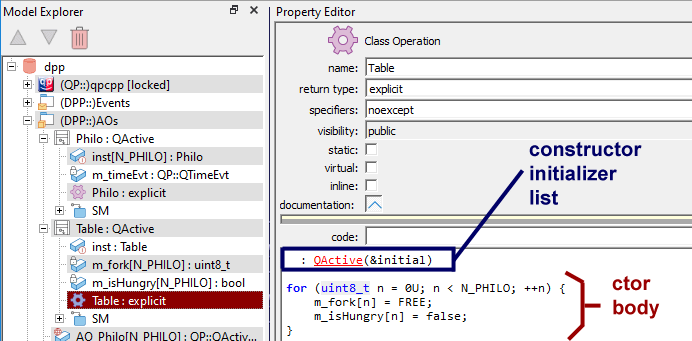
This piece of the model generates the following code:
You can make a C++ constructor explicit by providing the keyword explict in the return type filed in the Property Sheet. An example of an explicit constructor is provided in the Table constructor shown in the screen shot above.
A destructor is a kind of class operation that cleans up after an instance of its class. QM supports class destructors both for C and C++.
In C, a destructor should be named xtor. The xtor class operation should have return type void and should not take any parameters (except of the implicit me pointer).
In C++, a destructor should be named ~<Class>. The destructor class operation should have no return type and should not take any parameters (except of the implicit this pointer).
Static class operation does not have access to any specific instance of a class, but has permissions to access any attributes of any instance of the class. In C, a static class operation does not take the "me" pointer. Similarly, in C++, a static class operation does not take the implicit "this" pointer. You make a given class operation static by checking the static checkbox in the Class Operation Property Sheet.
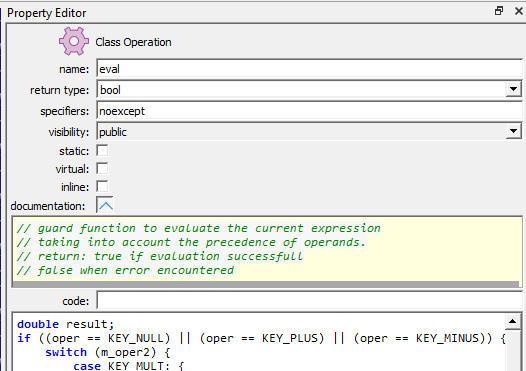
The class operation property sheet allows you to set the following properties:
override, noexcept, =delete, =0, etc.