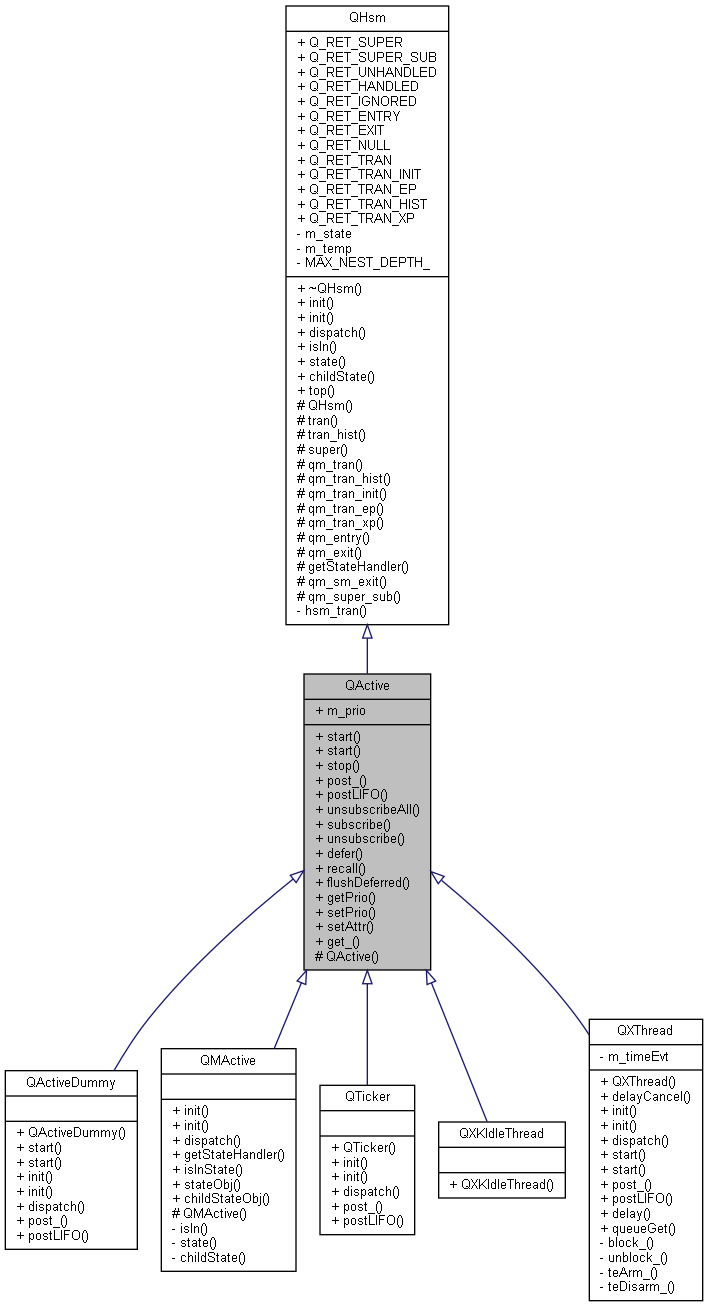
QActive active object (based on QP::QHsm implementation) More...
#include <qf.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual void | start (std::uint_fast8_t const prio, QEvt const **const qSto, std::uint_fast16_t const qLen, void *const stkSto, std::uint_fast16_t const stkSize, void const *const par) |
| Starts execution of an active object and registers the object with the framework. More... | |
| virtual void | start (std::uint_fast8_t const prio, QEvt const **const qSto, std::uint_fast16_t const qLen, void *const stkSto, std::uint_fast16_t const stkSize) |
| Overloaded start function (no initialization event) More... | |
| void | stop (void) |
| Stops execution of an active object and removes it from the framework's supervision. More... | |
| virtual bool | post_ (QEvt const *const e, std::uint_fast16_t const margin, void const *const sender) noexcept |
| virtual void | postLIFO (QEvt const *const e) noexcept |
| Posts an event directly to the event queue of the active object using the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) policy. More... | |
| void | unsubscribeAll (void) const noexcept |
| Un-subscribes from the delivery of all signals to the active object. More... | |
| void | subscribe (enum_t const sig) const noexcept |
Subscribes for delivery of signal sig to the active object. More... | |
| void | unsubscribe (enum_t const sig) const noexcept |
Un-subscribes from the delivery of signal sig to the active object. More... | |
| bool | defer (QEQueue *const eq, QEvt const *const e) const noexcept |
| Defer an event to a given separate event queue. More... | |
| bool | recall (QEQueue *const eq) noexcept |
| Recall a deferred event from a given event queue. More... | |
| std::uint_fast16_t | flushDeferred (QEQueue *const eq) const noexcept |
| Flush the specified deferred queue 'eq'. More... | |
| std::uint_fast8_t | getPrio (void) const noexcept |
| Get the priority of the active object. More... | |
| void | setPrio (std::uint_fast8_t const prio) |
| Set the priority of the active object. More... | |
| void | setAttr (std::uint32_t attr1, void const *attr2=nullptr) |
| Generic setting of additional attributes (useful in QP ports) More... | |
| QEvt const * | get_ (void) noexcept |
| Get an event from the event queue of an active object. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from QHsm Public Member Functions inherited from QHsm | |
| virtual | ~QHsm () |
| virtual destructor More... | |
| virtual void | init (void const *const e, std::uint_fast8_t const qs_id) |
| executes the top-most initial transition in QP::QHsm More... | |
| virtual void | init (std::uint_fast8_t const qs_id) |
| overloaded init(qs_id) More... | |
| virtual void | dispatch (QEvt const *const e, std::uint_fast8_t const qs_id) |
| Dispatches an event to QHsm. More... | |
| bool | isIn (QStateHandler const s) noexcept |
| Tests if a given state is part of the current active state configuration. More... | |
| QStateHandler | state (void) const noexcept |
| Obtain the current state (state handler function) More... | |
| QStateHandler | childState (QStateHandler const parent) noexcept |
| Obtain the current active child state of a given parent. More... | |
Data Fields | |
| std::uint8_t | m_prio |
| QF priority (1..QF_MAX_ACTIVE) of this active object. More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| QActive (QStateHandler const initial) noexcept | |
| protected constructor (abstract class) More... | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from QHsm Protected Member Functions inherited from QHsm | |
| QHsm (QStateHandler const initial) noexcept | |
| Protected constructor of QHsm. More... | |
| QState | tran (QStateHandler const target) noexcept |
| Helper function to specify a state transition. More... | |
| QState | tran_hist (QStateHandler const hist) noexcept |
| Helper function to specify a transition to history. More... | |
| QState | super (QStateHandler const superstate) noexcept |
| Helper function to specify the superstate of a given state. More... | |
| QState | qm_tran (void const *const tatbl) noexcept |
| Helper function to specify a regular state transition in a QM state-handler. More... | |
| QState | qm_tran_hist (QMState const *const hist, void const *const tatbl) noexcept |
| Helper function to specifiy a transition to history in a QM state-handler. More... | |
| QState | qm_tran_init (void const *const tatbl) noexcept |
| Helper function to specify an initial state transition in a QM state-handler. More... | |
| QState | qm_tran_ep (void const *const tatbl) noexcept |
| Helper function to specify a transition to an entry point to a submachine state in a QM state-handler. More... | |
| QState | qm_tran_xp (QActionHandler const xp, void const *const tatbl) noexcept |
| Helper function to specify a transition to an exit point from a submachine state in a QM state-handler. More... | |
| QState | qm_entry (QMState const *const s) noexcept |
| Helper function to specify a state entry in a QM state-handler. More... | |
| QState | qm_exit (QMState const *const s) noexcept |
| Helper function to specify a state exit in a QM state-handler. More... | |
| virtual QStateHandler | getStateHandler () noexcept |
| Get the current state handler of the HSM. More... | |
| QState | qm_sm_exit (QMState const *const s) noexcept |
| Helper function to specify a submachine exit in a QM state-handler. More... | |
| QState | qm_super_sub (QMState const *const s) noexcept |
| Helper function to call in a QM state-handler when it passes the event to the host submachine state to handle an event. More... | |
Friends | |
| class | QF |
| class | QTimeEvt |
| class | QTicker |
| class | QActiveDummy |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from QHsm Static Public Member Functions inherited from QHsm | |
| static QState | top (void *const me, QEvt const *const e) noexcept |
| the top-state. More... | |
 Static Public Attributes inherited from QHsm Static Public Attributes inherited from QHsm | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_SUPER {static_cast<QState>(0)} |
| event passed to the superstate to handle More... | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_SUPER_SUB {static_cast<QState>(1)} |
| event passed to submachine superstate More... | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_UNHANDLED {static_cast<QState>(2)} |
| event unhandled due to a guard evaluating to 'false' More... | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_HANDLED {static_cast<QState>(3)} |
| event handled (internal transition) More... | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_IGNORED {static_cast<QState>(4)} |
| event silently ignored (bubbled up to top) More... | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_ENTRY {static_cast<QState>(5)} |
| state entry action executed More... | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_EXIT {static_cast<QState>(6)} |
| state exit action executed More... | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_NULL {static_cast<QState>(7)} |
| return value without any effect More... | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_TRAN {static_cast<QState>(8)} |
| regular transition taken More... | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_TRAN_INIT {static_cast<QState>(9)} |
| initial transition taken More... | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_TRAN_EP {static_cast<QState>(10)} |
| entry-point transition into a submachine More... | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_TRAN_HIST {static_cast<QState>(11)} |
| transition to history of a given state More... | |
| static constexpr QState | Q_RET_TRAN_XP {static_cast<QState>(12)} |
| exit-point transition out of a submachine More... | |
 Protected Types inherited from QHsm Protected Types inherited from QHsm | |
| enum | ReservedHsmSignals : QSignal { Q_ENTRY_SIG = 1 , Q_EXIT_SIG , Q_INIT_SIG } |
QActive active object (based on QP::QHsm implementation)
|
protectednoexcept |
protected constructor (abstract class)
Definition at line 44 of file qf_qact.cpp.
|
virtual |
Starts execution of an active object and registers the object with the framework.
| [in] | prio | priority at which to start the active object |
| [in] | qSto | pointer to the storage for the ring buffer of the event queue (used only with the built-in QP::QEQueue) |
| [in] | qLen | length of the event queue (in events) |
| [in] | stkSto | pointer to the stack storage (must be nullptr in QV) |
| [in] | stkSize | stack size [bytes] |
| [in] | par | pointer to an extra parameter (might be nullptr) |
Reimplemented in QXThread, and QActiveDummy.
|
inlinevirtual |
Overloaded start function (no initialization event)
Reimplemented in QXThread, and QActiveDummy.
| void stop | ( | void | ) |
Stops execution of an active object and removes it from the framework's supervision.
Definition at line 112 of file qutest.cpp.
|
virtualnoexcept |
| [in,out] | e | pointer to the event to be posted |
| [in] | margin | number of required free slots in the queue after posting the event. The special value QP::QF_NO_MARGIN means that this function will assert if posting fails. |
| [in] | sender | pointer to a sender object (used in QS only) |
margin argument is special and denotes situation when the post() operation is assumed to succeed (event delivery guarantee). An assertion fires, when the event cannot be delivered in this case.Reimplemented in QXThread, QActiveDummy, and QTicker.
Definition at line 90 of file qf_actq.cpp.
|
virtualnoexcept |
Posts an event directly to the event queue of the active object using the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) policy.
| [in] | e | pointer to the event to post to the queue |
Reimplemented in QXThread, QActiveDummy, and QTicker.
Definition at line 228 of file qf_actq.cpp.
|
noexcept |
Un-subscribes from the delivery of all signals to the active object.
|
noexcept |
Subscribes for delivery of signal sig to the active object.
sig to the event queue of the active object.| [in] | sig | event signal to subscribe |
The following example shows how the Table active object subscribes to three signals in the initial transition:
|
noexcept |
Un-subscribes from the delivery of signal sig to the active object.
sig to the event queue of the active object.| [in] | sig | event signal to unsubscribe |
sig will never be dispatched to the state machine of the active object after un-subscribing from that signal. The event might be already in the queue, or just about to be posted and the un-subscribe operation will not flush such events.Defer an event to a given separate event queue.
e to the QF-supported native event queue eq. QF correctly accounts for another outstanding reference to the event and will not recycle the event at the end of the RTC step. Later, the active object might recall one event at a time from the event queue.| [in] | eq | pointer to a "raw" thread-safe queue to recall an event from. |
| [in] | e | pointer to the event to be deferred |
An active object can use multiple event queues to defer events of different kinds.
Definition at line 77 of file qf_defer.cpp.
|
noexcept |
Recall a deferred event from a given event queue.
eq and posted (LIFO) to the event queue of the active object.| [in] | eq | pointer to a "raw" thread-safe queue to recall an event from. |
Definition at line 113 of file qf_defer.cpp.
|
noexcept |
Flush the specified deferred queue 'eq'.
| [in] | eq | pointer to a "raw" thread-safe queue to flush. |
Definition at line 178 of file qf_defer.cpp.
|
inlinenoexcept |
|
inline |
| void setAttr | ( | std::uint32_t | attr1, |
| void const * | attr2 = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Generic setting of additional attributes (useful in QP ports)
|
noexcept |
Get an event from the event queue of an active object.
Definition at line 313 of file qf_actq.cpp.
|
friend |
| std::uint8_t m_prio |
QF priority (1..QF_MAX_ACTIVE) of this active object.